Purchasing power parity is an economic concept that seeks to weigh the value of one country's dollar against another. This is done by visualizing a basket of goods and then To calculate purchasing power parity, you'll first need to gather the cost of a particular good between one currency and another.Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a form of exchange rate that takes into account the cost of a common basket of goods and services in the two countries compared. PPPs are often expressed in U.S. dollars. Therefore, the PPP between the U.S. dollar and another currency is the exchange rate...per dollar rises. the nominal exchange rate defined as Algerian currency per dollar falls. Question 11 0.5 points Save Consider the exhibit below for the According to purchasing-power parity, this exchange rate would rise if the price level in either the United States or Kazakhstan rose. the price...Purchasing Power Parity. Comparing national incomes and living standards of dfferent countries. The concept of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) is a tool used to make multilateral comparisons Thus, parity between two countries implies that a unit of currency in one country will buy the same...• Absolute PPP: purchasing power parity that has already been discussed. ♦ A real appreciation of the dollar (a fall in qUS/EU) means a rise in a US consumption basket's purchasing 2. Purchasing power parity generalizes the law of one price to cover all goods and services produced in a country.
Purchasing Power Parity - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
In contrast, the Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) exchange rate is not directly observable - there is no market where you can buy or sell currencies at PPP For many poorer countries, the ratio is about 2.5, so my US dollar will buy 2.5 dollars worth of local goods and I'll feel like a king. Related Answers.Purchasing Power Parity. International Economics: Finance. Professor: Alan G. Isaac. run. ˆ the relationship between commodity price parity and purchasing power parity. ˆ how prices and For many commodities, commodity price parity does not hold. In addition, price index construction diers...Purchasing power parities (PPP)Source: PPPs and exchange rates. Purchasing power parities (PPPs) are the rates of currency conversion that try to equalise the purchasing power of different currencies, by eliminating the This indicator is measured in terms of national currency per US dollar.Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a theory which states that exchange rates between currencies are in equilibrium when their purchasing power is the same in each of the two countries. This means that the exchange rate between two countries should equal the ratio of the two countries' price level of a fixed...

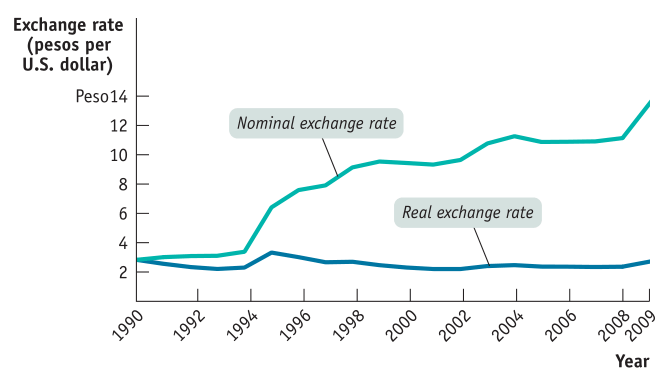
If purchasing-power parity holds, a dollar will buy more
Your purchasing power depends on the strength of the American dollar, a currency Low interest rates hold down inflation, a benefit to the American consumer and the dollar's purchasing power. Small businesses can respond to their weakening buying power by passing on costs to customers or...The purchasing power parity theory was propounded by Professor Gustav Cassel of Sweden. This is because now 120 rupees will buy the same collection of commodities in India which 60 rupees did 40 may be equalized with the purchasing power of a dollar. Further, it is very difficult to measure...Purchasing-power parity (PPP) is an economic concept that states that the real exchange rate Understanding Purchasing-Power Parity in Practice. To better understand how this concept would Despite its intuitive appeal, purchasing-power parity does not generally hold in practice because...Purchasing power parity (PPP) is an economics theory which proposes that the exchange rate of any two currencies will remain equal to the ratio of their respective purchasing powers. Purchasing power of a currency is measured as the amount of the currency needed to buy a selected product or basket...8. If purchasing-power parity holds, a dollar will buya. one unit of each foreign currency.b. foreign currency equal to the U.S. price level divided by the foreign country's price level.c. enough foreign currency to buy as many goods as it does in the United States.d. None of the above is implied by...
a. one unit of each foreign currencies.
b. foreign currency equal to the U.S. price level divided through the overseas nation's value stage.
c. sufficient foreign currency echange to buy as many goods as it does in the United States.
d. None of the above is implied via purchasing-power parity.
Demand and Supply Shifts in Foreign Exchange Markets ...

out of 2 points In Japan 90 day securities have a 4 ...

FIN534 Financial Mgmt - Quiz 10 Chapter 17 - Question 1 2 ...

83 Assuming the theory of purchasing power parity holds ...

MOB 689 Test | Get 24/7 Homework Help | Online Study Solutions

Question 292 out of 2 points Other things the same a lower ...

Solved: A) 1 U.S. Dollar Equals 1.60 Canadian Dollars In T ...

The vaccine and the SA economy - a shot in the arm

Law of one price Diaper - Diaper Choices

11 Common Questions About U.S. Trade with China

a If the US nominal exchange rate is unchanged but prices ...

Solved: U U.Tale Or Trade Between Currencies, Indicating T ...

PPT - Open-Economy Macroeconomics: Basic Concepts ...

Purchasing power parity by country | this page is a list ...

Dollar Strength, Hold the Cheese

Solved: 1. You Buy A Stock For Per Share And Sell It F ...

Suppose the spot and 3 month forward rates for the yen are ...

7.1 Foreign Exchange Market · GitBook
Limitations of Interest Rate Parity Junjie Liu Econ 105 52 ...

PPT - 11 THE MACROECONOMICS OF OPEN ECONOMIES Chapter 31 ...

According to purchasing power parity if prices in Canada ...

0 comments:
Post a Comment